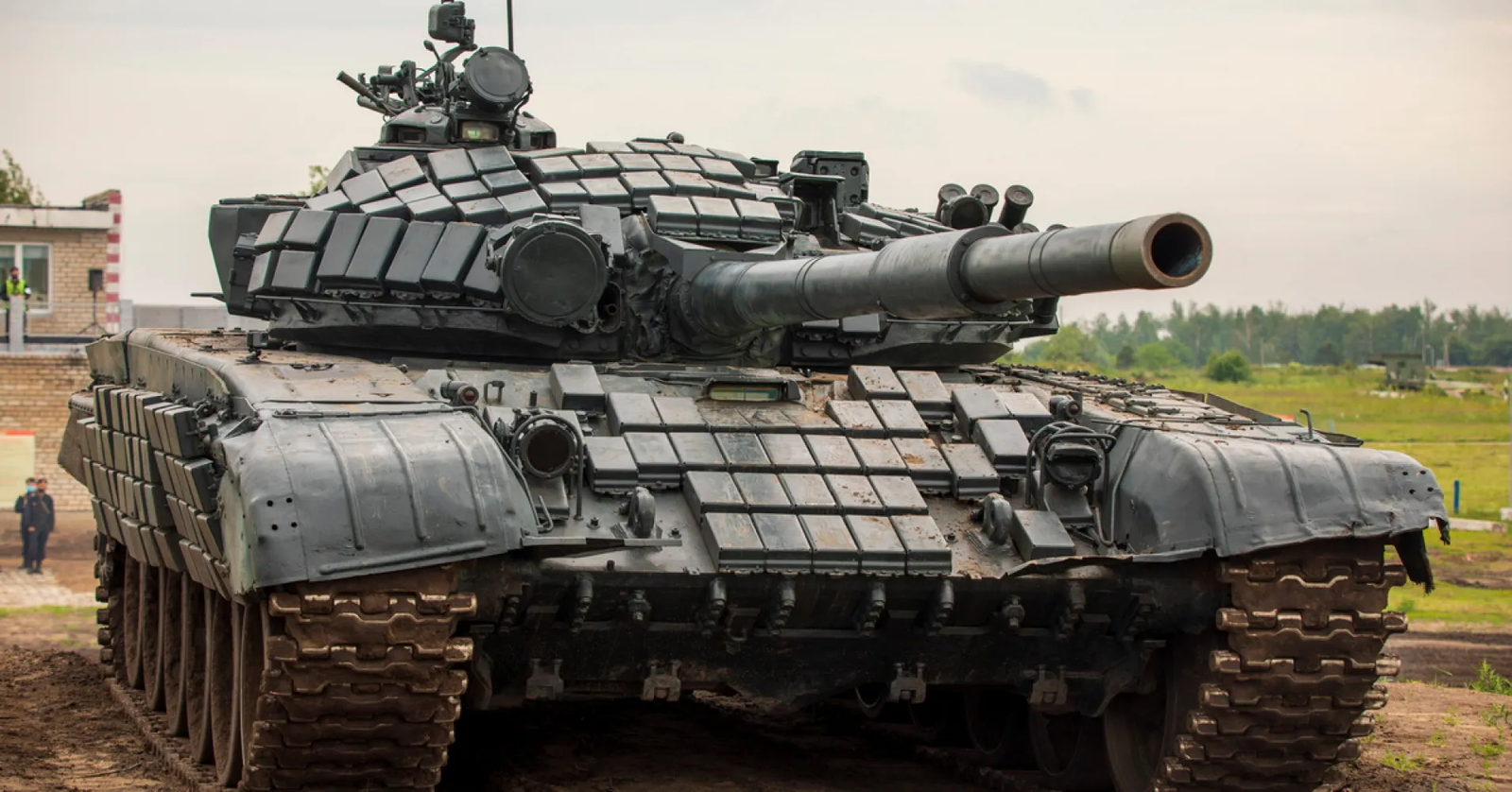
The T-72B main battle tank is not just an effective weapon system – it is a symbol of the architects’ endurance and fighting ground adaptability. Conceptualized during the Cold War riot, it should have been long gone from the face of the planet by the 21st century, this titan keeps proving time and time again that it is still very much alive and kicking. As is the case with the T-72B, the development of armored vehicles is an ongoing process that requires the balancing of firepower, protection, and mobility in ever-changing battlefields. Throughout its usage in the 1980s until its current missions in Ukraine, the T-72B has not only survived under modern combat conditions but also kept its operational abilities intact.

The T-72 was initially supposed to be a simpler and cheaper version of the complex but unreliable T-64. It was built to be tough, quick, and simple to handle, even with crews that had little training by the way of 1973 off the assembly lines. Nevertheless, the first editions were not near to being perfect. The fire control was rudimentary, the night vision was almost negligible, and the armor was only effective against minor weapons. The launch of anti-tank guided missiles like the TOW and MILA exposed these vulnerabilities, prompting the engineers to make a series of modifications to the tank.

The T-72B managed to eliminate the majority of shortcomings of the T-72 in 1984. The “Super Dolly Parton,” as the reinforced composite armor was jokingly called because of the turret’s cheek plates, provided the vehicle with much more protection. The initial fitting of the KONTAKT-1 explosive reactive armor (ERA) formed an additional barrier against the penetrative power of the contemporary anti-tank rounds, thereby raising the effective armor to roughly 700–900mm of the most common threats. The enhancements made the T-72B significantly stronger and trustworthy in the war zone, although it is still not an invincible tank.

Those T-72Bs were not identically constructed. For example, the T-72S ‘Shilden’ export model had a lighter ERA with some other characteristics adjusted to meet the requirements of foreign. The tanks were widely used in Polish, Czech, and East German units, each with its own tactics: Polish crews often chose to perform courageous and aggressive assaults, the Czech army relied mostly on large formations to keep morale high, and the East Germans put a lot of emphasis on exact, controlled breakthroughs. They were regularly patched up over the years to make them still reliable and keep them running even decades after the first deployment. At present, the T-72B is still highly regarded worldwide.

The fact that it still serves in Ukraine is maybe the most telling example of how the platform can be turned into an instrument of different situations or changed needs. The Americans, for example, financed refurbished Czech-made T-72Bs for the Ukrainian troops because dropping in a brand new tank system would have been very costly and slow, plus the necessity of a long training period. The Ukrainian crews familiar with the T-72 platform are good to go as they can directly start the operations, thus keeping the level with the Russian units using the same sets.

Modern battle has brought in the likes of drones, electronic warfare, and precision-guided weapons, which have become serious challenges to the traditional armored forces, and maybe they have rendered tanks like the T-72B obsolete.

Still, upgrades such as ERA, urban armor kits, and counter-IED systems keep them in the fight. These FPV drones that take most of the limelight are not free from technical failures; jamming, and operator skills constrain them too. Mortars and light artillery are among the few old-fashioned and yet steady, reliable threats that still exist alongside new weapons.

The duration of the conflict and the stress it caused on the two sides are other factors that have resulted in bringing back support tanks that are already old, some even without the latest optical or thermal imaging equipment. To illustrate, the Russian military started installing SOSNA-U thermal sights on their tanks in 2022, but had to reintroduce old models into the fight because of the realities of combat.

It is in such harsh conditions that qualities such as the training of the crew, the efficiency of optics, and fire control may decide on the outcome just as much as the armor. The fact that the T-72B is still being used drives home the point of the value of simplicity and rugged design.

While Western tanks like the Leopard 2 or M1 Abrams are equipped with cutting-edge technology, their complex nature and logistical needs can hinder the speed of deployment. On the other hand, the T-72B has a feature that makes it very special—it integrates a simple and sturdy design with incremental improvements that give it the flexibility and the reliability of both safety and offense.

As time progresses, the trend of modern warfare and technology, the T-72B, and basically all battle tanks, will still be forced to transform. Thus, the future of the tank would also entail dealing with drone swarms, electronic warfare, and precision-guided weapons. The historical record, however, suggests that if proper upgrades and planning are in place, then a well-constructed and resilient tank like the T-72B shall still be a relevant and daunting force in today’s warfields.