High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Often referred to as the “silent killer,” hypertension typically has no obvious symptoms but can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. This comprehensive guide will delve into the symptoms of high blood pressure, its underlying causes, and effective remedies to manage and prevent this condition.
What is High Blood Pressure?
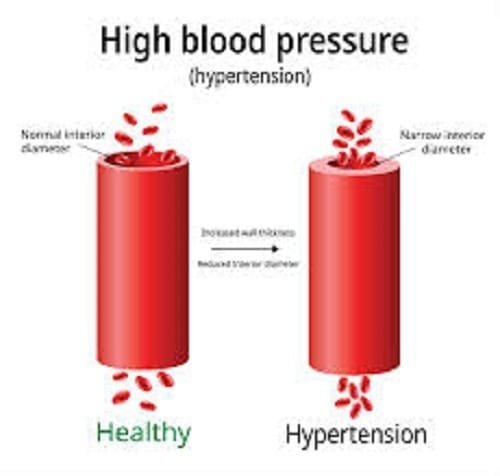
Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and is represented by two numbers: systolic pressure (the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats) over diastolic pressure (the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats). Normal blood pressure is generally considered to be around 120/80 mm Hg. Hypertension is diagnosed when blood pressure readings consistently exceed 130/80 mm Hg.
Types of Hypertension
- Primary Hypertension: This is the most common type and develops gradually over many years. It has no identifiable cause but is influenced by various genetic and environmental factors.
- Secondary Hypertension: This type occurs suddenly and is often caused by an underlying condition, such as kidney disease, hormonal disorders, or certain medications.
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
Hypertension is often called a “silent” condition because many people experience no symptoms until serious health issues arise. However, some individuals may report the following symptoms, especially when blood pressure reaches dangerous levels:
1. Headaches
Chronic headaches can occur, particularly in the back of the head or in the morning. These headaches may worsen with time and can be a sign of significantly elevated blood pressure.
2. Dizziness or Lightheadedness
Feeling dizzy, lightheaded, or experiencing a sense of imbalance can occur when blood pressure spikes or drops suddenly.
3. Shortness of Breath
High blood pressure can lead to heart strain, causing individuals to feel breathless during regular activities or even at rest.
4. Nosebleeds
While not a common symptom, frequent or unexplained nosebleeds can sometimes indicate hypertension.
5. Chest Pain
Severe chest pain can occur when hypertension contributes to heart problems, though this is usually a sign of an emergency requiring immediate medical attention.
6. Blurred Vision
High blood pressure can affect the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurred vision or other vision changes.
7. Fatigue
Constant fatigue or confusion can sometimes result from the heart and body being under stress due to prolonged hypertension.
Causes of High Blood Pressure
Understanding the underlying causes of hypertension is essential for effective management and prevention. While some factors are unavoidable, many can be controlled through lifestyle choices and medical interventions.
1. Uncontrolled Risk Factors
- Genetics: A family history of high blood pressure can increase your risk.
- Age: The risk of hypertension increases as you age, particularly after age 45 for men and 65 for women.
2. Lifestyle Factors
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional strain on the heart and can contribute to higher blood pressure.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and increased blood pressure.
- Diet: A diet high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats can elevate blood pressure levels.
3. Other Medical Conditions
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can lead to fluid retention, increasing blood pressure.
- Hormonal Disorders: Conditions such as hyperthyroidism or Cushing’s syndrome can affect blood pressure.
- Sleep Apnea: This condition causes interruptions in breathing during sleep, which can increase blood pressure.
4. Environmental and Psychological Factors
- Chronic Stress: Ongoing stress can lead to temporary spikes in blood pressure and may contribute to long-term hypertension.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Both can damage blood vessels and lead to elevated blood pressure levels.
Remedies for Managing High Blood Pressure
Managing high blood pressure involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and regular monitoring. Here are some effective remedies and strategies to help lower blood pressure and maintain a healthy heart:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy Diet
- DASH Diet: The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing sodium and saturated fats.
- Reduce Sodium Intake: Aim for less than 2,300 mg of sodium per day, and ideally limit intake to 1,500 mg for optimal blood pressure control.
Regular Exercise
- Aerobic Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, for at least 150 minutes per week can help lower blood pressure.
- Strength Training: Incorporating resistance training at least two days a week can also contribute to overall cardiovascular health.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Weight Management: Losing even a small amount of weight (5-10% of body weight) can significantly lower blood pressure and improve heart health.
2. Stress Management
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress and lower blood pressure.
- Regular Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, as poor sleep can negatively impact blood pressure.
3. Medication
If lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, your doctor may prescribe medications to help manage high blood pressure. Common types of antihypertensive medications include:
- Diuretics: Help the body eliminate excess sodium and water to reduce blood volume.
- ACE Inhibitors: Help relax blood vessels by blocking the formation of a hormone that narrows blood vessels.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Relax blood vessels by affecting the muscles in the artery walls.
- Beta-Blockers: Reduce heart rate and the force of contraction, leading to lower blood pressure.
4. Regular Monitoring
- Home Blood Pressure Monitoring: Invest in a home blood pressure monitor to track your levels regularly. This can help you and your healthcare provider understand how well your management strategies are working.
- Routine Check-Ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help identify potential issues before they become serious.
5. Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation—up to one drink per day for women and two for men.
- Quit Smoking: Stopping smoking can improve overall heart health and lower blood pressure.
When to Seek Medical Help
While lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage high blood pressure, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for guidance, especially if you experience symptoms or have a family history of hypertension. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe headache
- Chest pain or pressure
- Difficulty breathing
- Vision changes
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
Conclusion
High blood pressure is a significant health issue that requires attention and proactive management. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and effective remedies, individuals can take control of their heart health and reduce their risk of serious complications. Regular monitoring, lifestyle changes, and appropriate medical interventions are key to successfully managing high blood pressure. If you suspect you have hypertension or are at risk, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support. Your heart health matters make it a priority today!
Thanks for visiting Gymbag4u.com
You may also like reading other articles. https://gymbag4u.com/understanding-blood-pressure-on-world-hypertension-day-17-may/ and https://gymbag4u.com/dash-diet-lowering-blood-pressure-and-enhancing-health/ and https://gymbag4u.com/normal-blood-pressure-range-by-age-understanding-your-numbers/ and https://gymbag4u.com/foods-to-lower-high-blood-pressure-your-guide-to-a-healthier-heart/ and https://gymbag4u.com/how-to-control-the-high-bp-and-low-blood-pressure/