All about UTIs, urine infection symptom, causes, and remedies
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections, affecting millions of people each year. They can range from mild to severe and have a significant impact on overall health and quality of life. This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about UTIs, including urine infection symptom, causes, and remedies.
Understanding UTIs
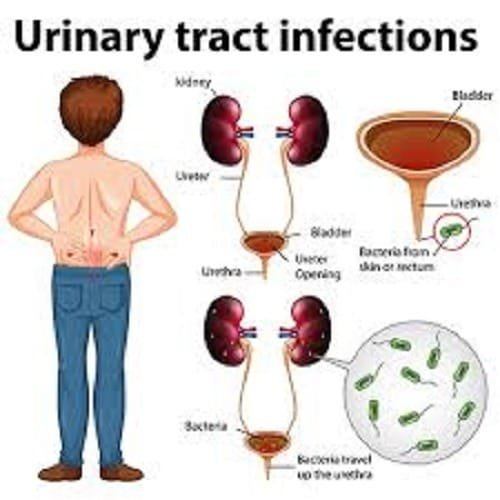
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Although the urinary tract is designed to keep out bacteria, sometimes these bacteria can invade and cause an infection.
Types of UTIs
- Cystitis: This is an infection of the bladder, the most common type of UTI.
- Urethritis: This infection affects the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body.
- Pyelonephritis: A more severe type of UTI, it infects the kidneys and can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Symptoms of UTIs
UTIs can present with a range of symptoms, which vary depending on the type and severity of the infection.
Common urine infection symptom:
- Frequent Urge to Urinate: You may feel an urgent need to urinate, often producing only small amounts of urine.
- Burning Sensation: A burning or stinging sensation during urination is a hallmark sign of a UTI.
- Cloudy or Dark Urine: Your urine may appear cloudy or dark and might have a strong, unpleasant odor.
- Pelvic Pain: Women may experience pain in the pelvic region, while men might feel discomfort in the rectal area.
- Lower Abdominal Pain: Some people report pain or cramping in the lower abdomen.
Severe Symptoms
- Fever and Chills: A high fever and chills may indicate that the infection has spread to the kidneys.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can accompany more severe UTIs or pyelonephritis.
- Flank Pain: Pain in the back or side, especially around the lower ribs, may suggest a kidney infection.
Causes of UTIs
Several factors can contribute to the development of a UTI. Understanding these causes can help in both prevention and treatment.
Bacterial Infections
- Escherichia coli (E. coli): This bacterium is responsible for about 80-90% of UTIs. It normally lives in the intestines but can enter the urinary tract.
- Other Bacteria: Less common bacteria, such as Klebsiella, Proteus, and Enterococcus, can also cause UTIs.
Risk Factors
- Sexual Activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urethra, increasing the risk of infection.
- Female Anatomy: Women are at higher risk due to the shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily.
- Urinary Retention: Incomplete emptying of the bladder can provide a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and pressure on the urinary tract during pregnancy can increase susceptibility to UTIs.
- Menopause: Decreased estrogen levels can lead to changes in the urinary tract, increasing the risk of infection.
Other Contributing Factors
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of UTIs by affecting the immune system and creating a favorable environment for bacterial growth.
- Catheter Use: Using a urinary catheter can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Immunocompromised State: Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS, can make individuals more susceptible to UTIs.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing a UTI typically involves a combination of medical history, symptoms, and laboratory tests.
Diagnosis
- Urinalysis: A urine sample is tested for the presence of white blood cells, red blood cells, bacteria, and other indicators of infection.
- Urine Culture: This test identifies the specific type of bacteria causing the infection and helps determine the most effective antibiotic treatment.
- Imaging Tests: In recurrent or complicated cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans may be used to identify structural issues or abnormalities.
Treatment
- Antibiotics: The primary treatment for UTIs is antibiotics. The type and duration of antibiotic therapy depend on the severity of the infection and the specific bacteria involved.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract and can aid in recovery.
Home Remedies and Prevention
While medical treatment is essential, several home remedies and lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms and prevent future infections.
Home Remedies
- Cranberry Juice: Some studies suggest that cranberry juice can help prevent UTIs by preventing bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract. However, it is not a cure for an existing infection.
- Probiotics: Probiotics, such as those found in yogurt, can help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the urinary tract and gut.
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the lower abdomen can help relieve pain and discomfort associated with UTIs.
Prevention Tips
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute urine and flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from the anal area from spreading to the urethra.
- Urinate After Intercourse: This can help flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sexual activity.
- Avoid Irritants: Certain products, such as douches, spermicides, and heavily scented hygiene products, can irritate the urinary tract and increase the risk of infection.
- Wear Breathable Underwear: Cotton underwear allows for better airflow and can help reduce moisture, which can be a breeding ground for bacteria.
When to See a Doctor
While many UTIs can be managed with home remedies and over-the-counter treatments, certain situations warrant a visit to a healthcare professional:
- Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms persist despite treatment or home remedies, consult a doctor.
- Severe Symptoms: If you experience severe symptoms such as high fever, severe pain, or nausea and vomiting, seek medical attention promptly.
- Recurrent UTIs: Frequent UTIs, especially if they occur more than twice a year, may require further evaluation and a more comprehensive treatment plan.
- Complications: If you suspect a kidney infection or have underlying health conditions, professional medical advice is crucial.
Conclusion
Understanding UTIs, including urine infection symptom, causes, and remedies, is vital for effective prevention and management. While UTIs are common and often easily treatable, recognizing the signs early and taking appropriate action can prevent complications and promote better health. By combining medical treatment with preventative measures and healthy lifestyle choices, you can effectively manage and reduce the risk of UTI’s by timely identifying urine infection symptom. If you have any concerns or persistent symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice to ensure optimal care and recovery.
Thanks for visiting Gymbag4u.com
You may also love reading our following articles. https://gymbag4u.com/depression-common-signs-and-effective-home-remedies/ and https://gymbag4u.com/lung-cancer-symptoms-diagnosis-and-treatment/ and https://gymbag4u.com/figs-nutrition-amazing-health-benefits-of-figs-eating-daily/ and https://gymbag4u.com/high-glycemic-foods-what-you-need-to-know/ and https://gymbag4u.com/kidney-stones-causes-symptoms-treatments-and-prevention/