During World War II, America was racing to produce fighters capable of beating enemy planes. The Fisher P-75 Eagle was meant to be the new game-changer: sleek, powerful, and set to dominate the skies. Instead, it was a lesson learned: an ambitious, costly failure that yielded lessons, not victories.

The novel begins in 1942, when the Army Air Forces wanted to have a fighter with better climb and performance. Fisher Body Division of General Motors saw an opportunity to step into the field of aviation. Already known for making automobile bodies and Sherman tanks, Fisher wanted to make a refined airplane. They hired Don Berlin, a designer who had been involved in designing the Curtiss P-36 and P-40, to lead the design.

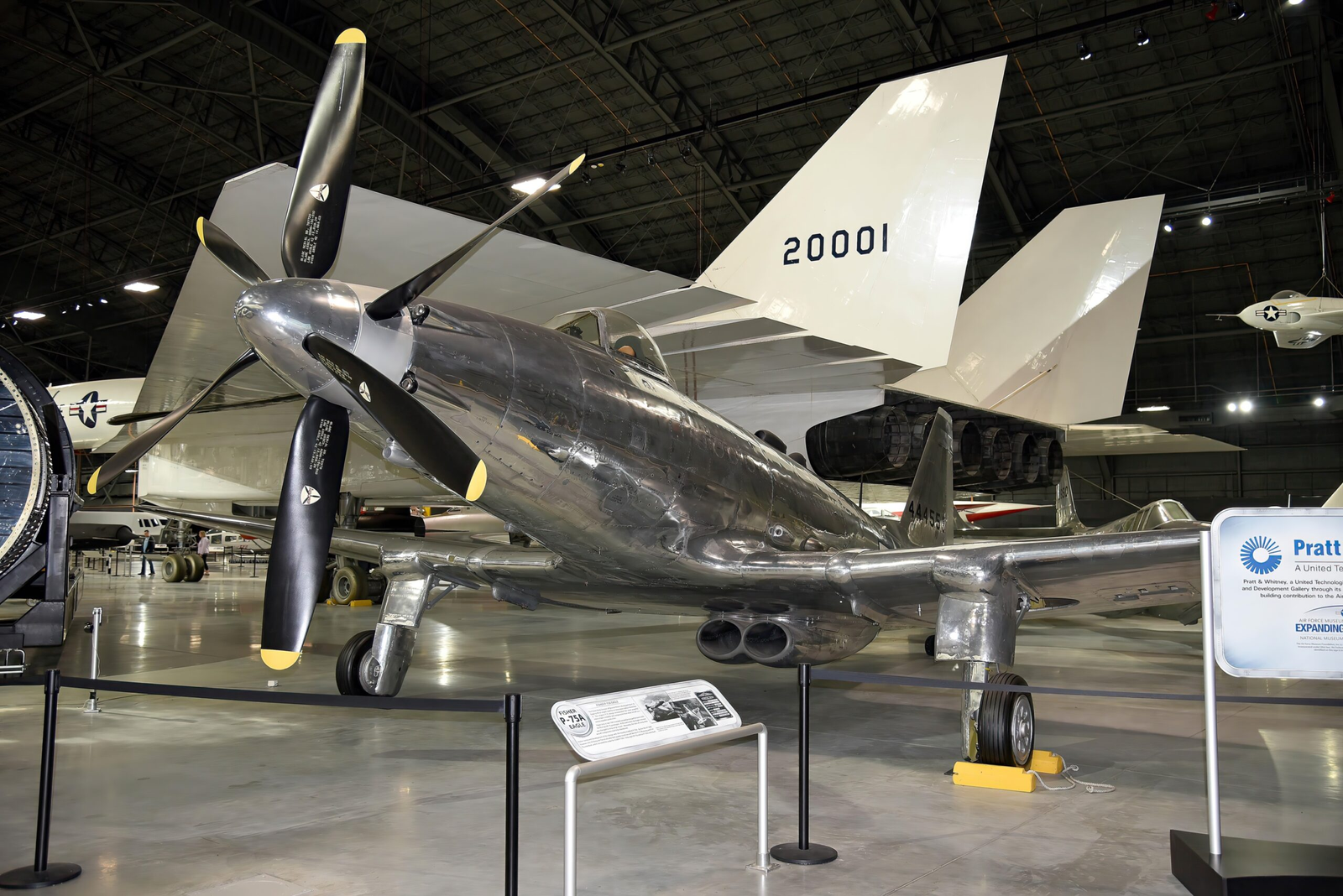
Fisher’s design was radical, if not too radical. The P-75 employed parts from various aircraft: P-40 Warhawk wings (subsequently replaced by Mustang wings), a tail section from the Douglas SBD Dauntless, and F4U Corsair landing gear.

Its engine, in the back of the cockpit, drove contra-rotating propellers via long extension shafts—a pilfered design from the Bell P-39. The goal was to increase production and have a war-ready airplane in the air in six months.

But airplanes aren’t automobiles, and what is true on the assembly line isn’t always true in flight. The Allison V-3420, basically two V-1710s installed in tandem, ran too hot and lacked power. The improv airframe created mushy flight, buggy spins, and slow roll rates. The center of gravity was also incorrect, and handling was dubious. In effect, the aircraft did not work.

As the war went on, the P-75 was reconfigured to be an escort with long range. It had increased fuel, a bubble canopy, a reconfigured tail, and a more powerful engine. Sadly, these improvements only added weight, complexity, and expense, deepening the issues of the airplane.

The military soon discovered it was more efficient, cost-effective, and practical to refine proven fighters such as the P-38 Lightning and the P-51 Mustang than it was to struggle with the P-75. Flight testing proved challenging: the initial prototype took to the skies in November 1943 but was unstable and lacking in satisfactory power.

There were a number of crashes during testing, some hazardous, and the aircraft never achieved its touted speed or climb rate.

By October 1944, the program was officially closed. Fewer than several dozen had been constructed, and the majority of them were destroyed. One restored specimen of the P-75 remains today at the National Museum of the United States Air Force in Dayton, Ohio.

The Fisher P-75 Eagle serves as a reminder that the assembly of spare parts from numerous disparate aircraft cannot suffice in place of rigorous, concerted design. Ambition and haste cannot be substitutes for ability, accuracy, and careful experimentation. Aviation historians refer to it as the “champion of spare parts fighters,” a chilling reminder of what may occur when ability is derailed by expediency.

Ultimately, the P-75 teaches us an ageless lesson: effective innovation mandates consistency of form, and success is sometimes best achieved by expanding upon successful prototypes—particularly when lives and triumph are on the line.