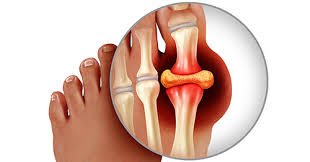
Gout: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling in the joints. It results from an excess of uric acid in the blood, which forms sharp crystals in the joints. Understanding gout’s causes, symptoms, treatments, and management strategies is crucial for effectively dealing with this condition and improving quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about gout.
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is a byproduct of purine metabolism, which is found in many foods. When uric acid levels become too high, it can lead to the formation of needle-like crystals that deposit in the joints, causing intense pain and inflammation.
Types of Gout
- Acute Gout: Characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain and inflammation in the affected joint. These attacks often occur at night and can last for a few days to a week.
- Chronic Gout: Occurs when gout is left untreated or poorly managed, leading to persistent inflammation and joint damage over time.
- Gouty Arthritis: A term used when gout attacks become frequent and lead to chronic joint pain and damage.
Causes of Gout
Gout is primarily caused by an excess of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. Various factors can contribute to elevated uric acid levels:
1. Dietary Factors
- High Purine Foods: Foods rich in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood (e.g., sardines, anchovies, and shellfish), can increase uric acid levels.
- Alcohol Consumption: Beer and spirits can raise uric acid levels, while wine has a lesser effect.
- Sugary Beverages: Drinks sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup can contribute to elevated uric acid levels.
2. Genetic Predisposition
Family history plays a role in the likelihood of developing gout. If close relatives have had gout, your risk of developing it increases.
3. Obesity
Excess body weight can lead to higher uric acid levels and increased risk of gout. Adipose tissue contributes to higher uric acid production and reduced excretion by the kidneys.
4. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase uric acid levels, including:
- Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can reduce the body’s ability to excrete uric acid.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can contribute to gout risk.
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can influence uric acid metabolism.
5. Medications
Some medications, such as diuretics (used to treat high blood pressure and edema) and certain drugs used for chemotherapy, can increase uric acid levels.
6. Dehydration
Inadequate fluid intake can lead to higher concentrations of uric acid in the blood, contributing to the risk of gout attacks.
Symptoms of Gout
Gout symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, but common signs include:
1. Sudden and Severe Pain
- Acute Attacks: Pain typically begins suddenly, often at night, and can be excruciating. The pain usually starts in one joint, commonly the big toe, but can affect other joints like the ankles, knees, and elbows.
2. Redness and Swelling
- Inflammation: The affected joint becomes red, swollen, and tender to the touch. The skin around the joint may appear shiny and inflamed.
3. Warmth
- Heat: The affected joint may feel warm to the touch due to inflammation.
4. Reduced Range of Motion
- Joint Stiffness: The joint may become stiff and difficult to move, limiting its range of motion.
5. Tophi (Chronic Gout)
- Crystal Deposits: In chronic cases, uric acid crystals can form lumps under the skin called tophi, which can cause joint deformity and discomfort.
Diagnosis of Gout
To diagnose gout, healthcare providers use a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
1. Joint Fluid Analysis
- Arthrocentesis: A sample of fluid from the affected joint is analyzed under a microscope to detect uric acid crystals.
2. Blood Tests
- Uric Acid Levels: Blood tests measure the level of uric acid in the blood. While elevated levels can indicate gout, they are not definitive as some people with high uric acid levels never develop gout.
3. Imaging Studies
- X-rays: Can help rule out other causes of joint pain and assess joint damage.
- Ultrasound: Can detect uric acid crystals in the joints and surrounding tissues.
- Dual-Energy CT Scan: Provides a detailed view of uric acid crystals and helps diagnose gout in difficult cases.
Treatment of Gout
Treating gout involves managing symptoms, reducing uric acid levels, and preventing future attacks. Treatment typically includes:
1. Medications
- Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, are used to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Colchicine: Effective for treating acute gout attacks and reducing inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Oral or injected corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation in severe cases.
- Urate-Lowering Medications: Medications like allopurinol or febuxostat help lower uric acid levels in the blood, preventing future gout attacks.
2. Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
- Dietary Modifications: Avoid high-purine foods and beverages, and limit alcohol and sugary drinks. Incorporate low-fat dairy products, whole grains, and plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help flush uric acid from the body and reduce the risk of attacks.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve overall health and support weight management.
3. Home Remedies
- Rest and Elevation: Rest the affected joint and elevate it to reduce swelling.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs to the inflamed joint for 15-20 minutes several times a day to alleviate pain and swelling.
- Epsom Salt Soaks: Soaking the affected joint in warm water with Epsom salts may provide temporary relief.
Prevention of Gout Attacks
Preventing gout attacks involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments and medical management:
1. Follow a Gout-Friendly Diet
- Avoid High-Purine Foods: Reduce intake of red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood.
- Increase Low-Purine Foods: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy into your diet.
2. Manage Weight and Exercise Regularly
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Work with a healthcare provider to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling to improve joint function and overall health.
3. Monitor Uric Acid Levels
- Regular Check-Ups: If prescribed urate-lowering medications, have regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor uric acid levels and adjust treatment as needed.
4. Limit Alcohol and Sugary Drinks
- Moderation: Limit alcohol consumption and avoid sugary beverages to help manage uric acid levels.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful and debilitating condition that requires careful management to prevent and treat attacks effectively. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of gout, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to prescribed treatments, and making dietary adjustments can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks. If you suspect you have gout or experience symptoms, consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Thanks for visiting Gymbag4u.com
You may also love reading our following articles. Leafy Green: Unveiling the Nutritional Champs of Your Diet – GymBag4U and What is sedentary lifestyle and its impact on our wellbeing – GymBag4U and Shoulder Pain: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing Discomfort – GymBag4U