embolism pulmonary disease cause and care
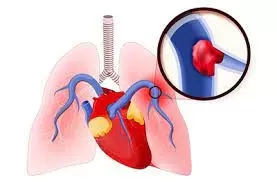
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the lungs. This blockage can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pulmonary embolism.
Causes of Pulmonary Embolism:
PE is usually caused by a blood clot that travels from another part of the body, usually the legs or pelvis. These blood clots, known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), can break off and travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, where they can cause a blockage.
Other factors that may increase the risk of developing PE include:
- Surgery or hospitalization
- Cancer or chemotherapy
- Trauma or injury
- Prolonged bed rest or immobility
- Hormonal medications, such as birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy
Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism:
The symptoms of PE can vary, depending on the size and location of the blood clot. Some people may not experience any symptoms, while others may experience:
- Shortness of breath, which may come on suddenly or gradually
- Chest pain, which may worsen with deep breathing or coughing
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Coughing up blood
- Lightheadedness or fainting
- Leg swelling or pain
Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism:
The primary goal of treatment for PE is to prevent further blood clots from forming and to remove existing blood clots. Treatment options may include:
- Anticoagulant medications – Medications such as heparin and warfarin may be prescribed to prevent blood clots from forming or growing.
- Thrombolytic therapy – In some cases, medication may be given to dissolve the blood clot.
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter – A small device may be inserted into the vena cava to catch blood clots before they can travel to the lungs.
- Surgery – In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a large blood clot from the lungs.
Prevention of Pulmonary Embolism:
There are several things you can do to help prevent PE, including:
- Moving around regularly – If you are bedridden or sitting for long periods, try to move your legs frequently to improve circulation.
- Maintaining a healthy weight – Being over weight increases the risk of developing PE.
- Quitting smoking – Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots.
- Taking precautions during travel – If you are traveling long distances by car or plane, make sure to move around regularly and stay hydrated.
In conclusion, pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. It is usually caused by a blood clot that travels from another part of the body. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, chest pain, and rapid heartbeat. Treatment options include anticoagulant medications, thrombolytic therapy, IVC filter placement, and surgery. If you are experiencing symptoms of PE, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
We hope our readers are now aware about pulmonary embolism health condition, which will help them to take care in such any emergency situation.
Thanks for visiting our website
GymBag4U – Your Fitness is Our Passion