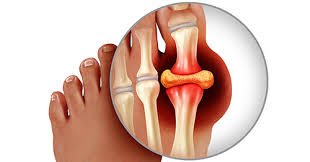
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints, most commonly the big toe. While gout can be painful and debilitating, it can be managed effectively with proper understanding, treatment, and lifestyle changes. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, treatments, and lifestyle changes associated with gout.
Causes of Gout: Unraveling the Crystal Formation
Gout occurs when urate crystals accumulate in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain. Urate crystals form when there is an excess of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. Some common causes and risk factors for gout include:
- Dietary Factors: Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and sugary beverages, can increase uric acid levels in the blood and contribute to the development of gout.
- Genetics: There appears to be a genetic component to gout, as it tends to run in families. Individuals with a family history of gout are at a higher risk of developing the condition themselves.
- Obesity: Excess weight can lead to increased production of uric acid and decreased excretion of uric acid by the kidneys, putting individuals at a higher risk of developing gout.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, can increase the risk of developing gout.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gout
Gout typically manifests with sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints, most commonly the big toe. Some common symptoms of gout include:
- Acute Joint Pain: The hallmark symptom of gout is intense pain, often described as sharp or stabbing, that typically affects one joint at a time, most commonly the big toe. The pain usually comes on suddenly and reaches its peak within 24 hours.
- Swelling and Redness: The affected joint may become swollen, red, and warm to the touch during a gout attack.
- Limited Range of Motion: Gout attacks can cause stiffness and difficulty moving the affected joint, making it challenging to perform daily activities.
- Recurrent Attacks: After the initial gout attack resolves, some individuals may experience recurrent attacks of gout in the same or different joints over time.
Treatment Options for Gout: Alleviating Pain and Preventing Attacks
While there is no cure for gout, treatment aims to relieve pain during acute attacks, reduce the frequency and severity of attacks, and lower uric acid levels in the blood to prevent future attacks and complications. Treatment options for gout may include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or indomethacin are often prescribed to help relieve pain and inflammation during acute gout attacks.
- Colchicine: Colchicine is a medication that can help reduce inflammation and pain during gout attacks, particularly when started early in the course of the attack.
- Corticosteroids: Oral or injectable corticosteroids may be prescribed for individuals who cannot tolerate NSAIDs or colchicine or who have severe gout attacks.
- Urate-Lowering Therapy (ULT): Urate-lowering medications such as allopurinol or febuxostat may be prescribed to lower uric acid levels in the blood and prevent future gout attacks. These medications are typically taken daily and may need to be continued long-term.
- Lifestyle Changes for Gout Management: Taking Charge of Your Health
In addition to medical treatments, incorporating certain lifestyle changes can help manage gout symptoms, reduce the frequency of gout attacks, and improve overall health. Some lifestyle changes that may be beneficial for gout management include:
- Dietary Modifications: Limiting consumption of high-purine foods such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and sugary beverages can help reduce uric acid levels in the blood and prevent gout attacks. Instead, focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water and staying well-hydrated can help prevent the formation of urate crystals in the joints and reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help reduce the risk of gout attacks, as excess weight is a risk factor for gout.
- Limiting Alcohol Intake: Alcohol, particularly beer and spirits, can increase uric acid levels in the blood and trigger gout attacks. Limiting alcohol consumption or avoiding it altogether can help prevent gout attacks.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or yoga, can help improve overall health, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of gout attacks.
In conclusion, gout is a common and painful form of inflammatory arthritis that can be managed effectively with proper understanding, treatment, and lifestyle changes. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gout, individuals can take charge of their health and reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks. If you suspect you have gout or are experiencing symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management. With the right support and guidance, individuals with gout can improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of this chronic condition.
Thanks for visiting Gymbag4u.com
You may also love reading our following articles. Leafy Green: Unveiling the Nutritional Champs of Your Diet – GymBag4U and What is sedentary lifestyle and its impact on our wellbeing – GymBag4U and Shoulder Pain: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing Discomfort – GymBag4U